初次接触RunLoop的概念,是在初步了解NSObject和学习手势识别时,看的一头雾水,现在总结一下内容。
RunLoop的定义
Run loops are part of the fundamental infrastructure associated with threads. A run loop is an event processing loop that you use to schedule work and coordinate the receipt of incoming events. The purpose of a run loop is to keep your thread busy when there is work to do and put your thread to sleep when there is none.
RunLoop在程序运行时,会进行消息处理,进入“等待消息-接收消息-处理的消息”的循环中,有消息就进行对应的处理,没有消息则进入睡眠状态。
RunLoop的事件源
这张图解释了RunLoop中事件的来源类型,大致包括了监听事件和定时器事件
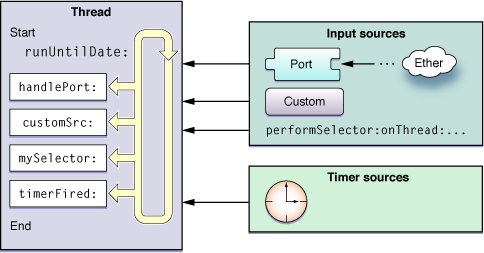
一个运行的RunLoop会打包消息,将消息传送给对应的接受者,进行处理
包含两种大类型,一种是线程或者其他应用传递的异步消息,另外一种是定时器的同步消息,在特定的时间执行,这两种都会在事件到达后,由程序来处理
具体的,可以看到input sources包含了以下类型
- port
- custom
- selector
Port
A CFMachPort object is a wrapper for a native Mach port (mach_port_t). Mach ports are the native communication channel for the macOS kernel.
port这种事件源是来自于系统内核的调度与事件传递
Custom
这种类型就是由开发人员发送的事件,CFRunLoopSource就是事件源,可以通过创建CFRunLoopSource对象实现向RunLoop发送事件
CFRunLoopSource包括两种类型,version0和version1
version0
Version 0 sources, so named because the version field of their context structure is 0, are managed manually by the application. When a source is ready to fire, some part of the application, perhaps code on a separate thread waiting for an event, must call CFRunLoopSourceSignal to tell the run loop that the source is ready to fire. The run loop source for CFSocket is currently implemented as a version 0 source.
大致就是这种类型的CFRunLoopSource在准备完成后会发送一个CFRunLoopSourceSignal,通知runloop,这个CFRunLoopSource已经准备好
version1
Version 1 sources are managed by the run loop and kernel. These sources use Mach ports to signal when the sources are ready to fire. A source is automatically signaled by the kernel when a message arrives on the source’s Mach port. The contents of the message are given to the source to process when the source is fired. The run loop sources for CFMachPort and CFMessagePort are currently implemented as version 1 sources.
这种类型的CFRunLoopSource会由系统内核自动的通过Mach ports来发送信号,通知runloop
这两种类型的CFRunLoopSource可以被多个runloop,多种runloop模式同时注册,当信号发出时,第一个收到消息的runloop就会对这个source进行处理
Selector
在NSObject中定义了一系列的performSelector,这些方法将会添加到runloop中执行,因此如果没有runloop,这些方法自然也就不会被执行了,也有例外情况,如下几个方法
1
2
3
4
5
performSelectorOnMainThread:withObject:waitUntilDone:
performSelectorOnMainThread:withObject:waitUntilDone:modes:
performSelector:onThread:withObject:waitUntilDone:
performSelector:onThread:withObject:waitUntilDone:modes:
这些方法是在指定的线程中执行对应的Selector,但是如果调用这些方法的线程和指定运行线程是同一个线程,方法会被直接执行,不添加到runloop。 这是很简单的道理,如果当前线程没有开启runloop,把selector添加进runloop的话将会导致selector不执行,然而线程还在等待,造成卡死;如果runloop已经开始,那么selector将会处于runloop的callout方法中,线程等待runloop从callout从调用selector,也是卡死线程
Timer
各类定时操作,会同步发送事件到线程并执行,timer可以设置执行一次或多次,重复执行的timer会有例外出现,即是任务执行的时间会以预定时间为准,而不是以第一次执行的时间为准
假设有一个重复执行的timer,在10s后开始第一次,执行第一次后每5s都重复执行一次
但是,第一次任务执行时出现了某些问题,导致延时执行
第14s时完成了第一次任务执行,那么第二次任务将在第一次任务执行后的1s执行
因为第二次任务的执行时间是在预定时间的5s后,即第10s的5s后,而不是第一次任务执行时的14s的5s后
如果第一次任务的执行是在16s,延迟超过了一个周期,任务将在延时后立即执行,然后等待下一个周期的任务
Observers
在runloop中,除了执行事件源,还会发出一系列通知,Observers就会监听它们,并对线程做额外的操作
观察者并不属于事件源,它适用于观察runloop的状态,包括了以下几种
- 进入runloop
- runloop将执行定时器
- runloop将执行事件源
- runloop将休眠
- runloop被唤醒
- runloop退出
要注意,在没有事件源的情况下,runloop是会在开启后直接退出的
RunLoop模式
RunLoop的模式适用于多种场景,并且事件源也可以通过RunLoop的模式来决定被处理与否
具体的模式包括了以下几种,这些模式有着不同的应用
- NSDefaultRunLoopMode
- NSConnectionReplyMode
- NSModalPanelRunLoopMode
- NSEventTrackingRunLoopMode
- NSRunLoopCommonModes
NSDefaultRunLoopMode
The default mode is the one used for most operations. Most of the time, you should use this mode to start your run loop and configure your input sources.
默认的模式,一般runloop都是此模式运行的
NSConnectionReplyMode
Cocoa uses this mode in conjunction with NSConnection objects to monitor replies. You should rarely need to use this mode yourself.
这个模式与NSConnection对象配合使用,用于监控回复,一般开发者用不到这个模式
NSModalPanelRunLoopMode
Cocoa uses this mode to identify events intended for modal panels.
这个模式用于Model Panel区分事件,在macOS开发会使用,暂时不了解
NSEventTrackingRunLoopMode
Cocoa uses this mode to restrict incoming events during mouse-dragging loops and other sorts of user interface tracking loops.
这个模式用于鼠标或者滑动等需要追踪的场景,比如ScrollView
NSRunLoopCommonModes
This is a configurable group of commonly used modes. Associating an input source with this mode also associates it with each of the modes in the group. For Cocoa applications, this set includes the default, modal, and event tracking modes by default. Core Foundation includes just the default mode initially. You can add custom modes to the set using the CFRunLoopAddCommonMode function.
这个模式是一组runloop的集合,可以通过CFRunLoopAddCommonMode这个方法对其添加
1
void CFRunLoopAddCommonMode(CFRunLoopRef rl, CFRunLoopMode mode);
第一个参数是要修改的runloop,每一个runloop中都存在自己的模式列表,第二个参数是要添加的模式
RunLoop模式的切换
通过以上的信息,一个runloop可以包括多种模式,多个任务、timer等事件源以及Observer
对于非主线程使用的runloop,可以通过退出当前runloop,重新进入来切换模式,也可以直接进入另一个模式,即嵌套
对于主线程,runloop的开始不受开发者控制,并且包括了很多系统的事件,模式切换由系统调用,主线程模式的切换是通过退出runloop后重新进入来完成的
什么时候使用RunLoop
一个线程对应着一个RunLoop对象,一个RunLoop有着多种模式,每种模式也有对应着他们的事件源
The only time you need to run a run loop explicitly is when you create secondary threads for your application.
苹果指出,唯一应该让RunLoop运行的时机是在给APP添加线程时,其中执行这些操作时,需要启动runloop对象
- 使用port或者custom的事件源来与其他线程通信
- 使用timer
- 使用performSelector系列方法,但是要注意此前提到的例外情况
- 线程保活